- 20 August 2024
- 1003 Views
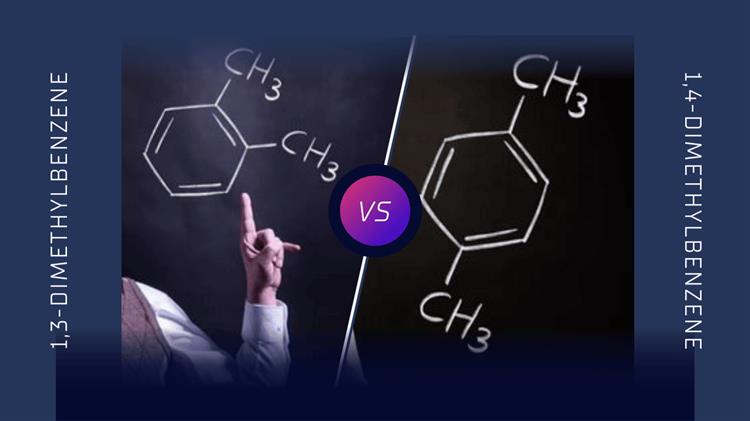
Isomerism is a fundamental concept in organic chemistry, where molecules with the same molecular formula can have different structural arrangements, leading to distinct physical and chemical properties. 1,3-Dimethylbenzene (meta-xylene) and 1,4-dimethylbenzene (para-xylene) are prime examples of such isomers. Both compounds share the molecular formula C8H10C_8H_{10}C8H10 but differ in the positions of their methyl groups on the benzene ring. This article delves into the structural differences between these two isomers and examines how these differences influence their properties, applications, and environmental impacts.
Structural Differences of 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene
Isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but differ in the arrangement of their atoms. 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene are positional isomers, where the difference lies in the positions of the methyl groups attached to the benzene ring.
1,3-Dimethylbenzene (Meta-Xylene): In this isomer, the methyl groups are attached to the 1st and 3rd carbon atoms of the benzene ring. This arrangement is known as the "meta" configuration, which places the two methyl groups at a 120-degree angle relative to each other.
1,4-Dimethylbenzene (Para-Xylene): Here, the methyl groups are attached to the 1st and 4th carbon atoms of the benzene ring. The "para" configuration positions the methyl groups directly opposite each other, at a 180-degree angle.
The structural differences between these isomers result in variations in their physical and chemical properties, which are explored in the following sections.
Physical Properties of 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene
The structural variations between 1,3-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene lead to differences in their physical properties:
Boiling and Melting Points: 1,4-Dimethylbenzene (para-xylene) typically has a higher melting point compared to 1,3-dimethylbenzene (meta-xylene) due to its more symmetrical structure, which allows for better packing in the solid state. However, both isomers have similar boiling points, reflecting their shared molecular size and weight.
Density: Para-xylene generally has a slightly higher density than meta-xylene, again due to its symmetrical structure, which results in more efficient molecular packing.
Solubility: Both isomers are poorly soluble in water but are soluble in organic solvents like ethanol, ether, and benzene. The slight structural differences do not significantly affect their solubility profiles in most solvents.
Other Physical Characteristics: Both isomers exhibit similar refractive indices and specific heat capacities, with only minor differences attributable to their structural configurations.
Chemical Properties of 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene
The chemical behavior of 1,3-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene is influenced by the positioning of the methyl groups, affecting how each compound interacts with other chemicals:
Reactivity: Both isomers undergo similar types of chemical reactions, such as electrophilic aromatic substitution, where the benzene ring reacts with electrophiles. However, the position of the methyl groups can influence the rate of reaction and the preferred substitution patterns.
Substitution Reactions: In electrophilic substitution reactions, meta-xylene tends to direct incoming substituents to the positions that are meta to the existing methyl groups, while para-xylene directs substituents to the ortho and para positions relative to the methyl groups.
Oxidation: The oxidation of both isomers typically leads to the formation of terephthalic acid, an important industrial chemical. However, the specific pathways and conditions required can vary slightly between the two isomers due to their structural differences.
Industrial and Practical Applications of 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene
The structural differences between 1,3-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene also have significant implications for their industrial uses:
Meta-Xylene (1,3-Dimethylbenzene): Meta-xylene is primarily used in the production of isophthalic acid, a precursor in the manufacture of resins, plastics, and synthetic fibers. It is also used as a solvent in various chemical processes and in the formulation of certain paints and coatings.
Para-Xylene (1,4-Dimethylbenzene): Para-xylene is more widely used than meta-xylene, particularly in the production of terephthalic acid, which is a key raw material in the manufacture of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastics and fibers. Para-xylene's more symmetrical structure makes it especially suited for this purpose, leading to its prominence in the plastics industry.
Importance in Manufacturing: The specific applications of these isomers are closely tied to their structural properties, making one isomer more suitable than the other for certain industrial processes.
Environmental and Health Impacts of 1,3-Dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene
Understanding the environmental and health impacts of 1,3-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene is crucial for safe handling and regulatory compliance:
Toxicity: Both isomers are considered toxic and can cause various health effects upon exposure, including respiratory issues, skin irritation, and potential neurological effects. Long-term exposure can lead to more severe health risks.
Environmental Impact: These compounds are relatively persistent in the environment and can contribute to pollution if not managed properly. Both isomers can be harmful to aquatic life and may contribute to air and water pollution through industrial emissions and accidental spills.
Regulatory Considerations: Due to their potential health and environmental risks, the handling and disposal of these chemicals are regulated by various governmental agencies. Compliance with these regulations is essential to minimize their impact on human health and the environment.
Buy Dimethylbenzene
When purchasing Dimethylbenzene , it is important to keep a few key points in mind. First, the quality of Dimethylbenzene should be checked, which includes its porosity and reactivity level. Also, the source of carbon production is very important; Make sure the Dimethylbenzene is produced from sustainable sources and with high environmental standards. The type of Dimethylbenzene (powder, granular, or block) should be selected according to the type of use and purification system.
In this regard, Elsapa Alzahbi is one of the reliable suppliers of Dimethylbenzene in the market, which offers a variety of products. Elsapa Alzahbi Dimethylbenzene are available in different types that are able to meet the different needs of water purification in the domestic, industrial and commercial sectors. Choosing Elsapa Alzahbi products can be a guarantee of obtaining high-quality purified water and optimizing the purification process in different sets.
in conclusion: The differences between 1,3-dimethylbenzene and 1,4-dimethylbenzene extend beyond mere structural variations. These differences influence their physical and chemical properties, industrial applications, and environmental impacts. Understanding these distinctions is essential for chemists, industrial manufacturers, and environmental scientists to make informed decisions about the use and management of these compounds.
